JLPT N5 Practice Test
Discover the essentials of JLPT N5 on this page, designed for beginners of Japanese language proficiency.
Here, we provide a concise overview of the exam’s structure and key components, along with a practice test to help you gauge your preparation.

All About JLPT N5 with the Practice Test
What Japanese Language Learners Need to Know to Pass JLPT N5
- What kind of test is the JLPT N5?
- What is the difficulty level of the JLPT N5?
- What is the difficulty level of the N5 exam?
- What is the difficulty level of the JLPT N5?
- What are the questions on the N5 exam?
- What level of Japanese proficiency can be expected from those who hold the JLPT N5?
All the questions that learners who want to pass the JLPT N5 exam need to know will be answered.
Click here for Japanese lessons with the best Japanese tutors for pasing the JLPT.
It is held twice a year, in early July and December.
To apply for the upcoming JLPT N5 exam, please click here:

Take the JLPT N5 practice test now
Let’s try a JLPT N5 mock test.
Vocabulary: 25 min, Grammar: 50min, Listening: 30min
This practice test is slightly different from the actual number of exam questions and question format on the actual N5 test. Please purchase the latest practice exam questions to make sure. Source: Japanese-Language Proficiency Test Worldwide Official Website.
If you have any questions, ask them for free! ➡ Japanese Question Form
Kanji List for Passing JLPT N5
This is a list of kanji required to pass JLPTN5. 79 kanji to memorize in order to pass the test.
Advantages of taking the JLPT N5
The exam is often taken to meet the requirements for becoming a candidate for nurses and care workers under the EPA (Economic Partnership Agreement).
The number of test takers for the JLPT (Japanese Language Proficiency Test)
The number of test takers for the JLPT continues to grow every year.
The reason for this is that the number of people learning Japanese is increasing every year.
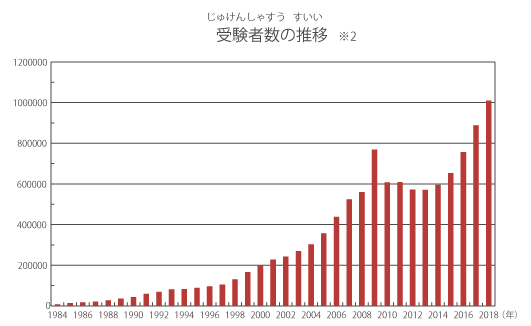
Refer to the JLPT official website.
- According to the latest data, the number of examinees per year exceeds about 1 million. (Exams held in July and December 2019)
- According to the latest data, the annual number of examinees is over 1 million.
- The number of examinees by level is as follows: N2, N3, N1, N4, and N5.
- JLPT N2 has the highest number of examinees, and JLPT N5 has the lowest number of examinees.
- In addition, the number of test takers by level is skewed by country and region.
- In East Asia, such as South Korea and China, the number of examinees taking the JLPT N1 and N2 tends to be higher.
- In Southeast Asia, such as Thailand and Vietnam, the number of examinees for JLPT N3, N4, and N5 is higher.
JLPT N5 Test Outline
| 言語知識(文字・語彙) | 20分 |
| 言語知識(文法)・読解 | 40分 |
| 聴解 | 30分 |
| 合計90分 |
Refer to the JLPT official website.
How difficult is the JLPT N5?
- N5 is the lowest level among N1 to N5.
- If you pass the N5 level, you can be certified as “able to understand basic Japanese to some extent.
Please refer to the text below for the specific level of “reading” and “listening” ability!
| Guidelines for JLPT N5 Certification | |
| Able to understand basic Japanese to some extent. | |
| Reading | Able to read and understand standardized words, sentences, and texts written in hiragana, katakana, and basic kanji used in daily life. |
| Listening | Able to listen to necessary information in short conversations spoken slowly in classrooms, in one’s surroundings, and in other situations often encountered in daily life. |
Refer to the JLPT official website.
As a whole, N4 to N5 are set as “the level to understand basic Japanese,” N3 as “daily conversation level Japanese,” and N1 to N2 as “the level to understand Japanese higher than daily conversation.
Passing Score and Pass Rate
- The JLPT N5 has a maximum score of 180 points, with a passing score of 80 points.
- It is not enough to have a total score of 80 points in all parts, but you must also be able to score at least the standard points in each part (38 points for language knowledge and reading comprehension, 19 points for listening comprehension).
| JLPT N5 Passing Score (JLPT N5の合格点) | |
| Score Classification 得点区分 | Score Range 得点の範囲 |
| Language knowledge (letters, vocabulary, grammar), reading comprehension 言語知識(文字・語彙・文法)・読解 | 0-120 (standard score: 38 points) |
| Listening comprehension 聴解 | 0~60 (standard score 19 points) |
| Total Score | 0~180 |
- The pass rate is about 41-56% every year.
- On average, one out of every two students passes the exam.
- Compared to the other levels, N5 has the highest pass rate.
What is the Japanese Language Proficiency Test (JLPT)?
Overview of the JLPT
The Japanese-Language Proficiency Test (JLPT) is a language proficiency test for non-native speakers of Japanese (Japanese nationals are also eligible to take the test).
- Sponsored by: Japan Educational Exchanges and Services and The Japan Foundation
- It has been conducted since 1984.
- Can be taken in Japan and in 87 countries and regions around the world
- Date of administration: Basically July and December (twice a year)
- English name: “Japanese-Language Proficiency Test (JLPT)
Features of the JLPT exam
There are a total of five levels in this exam. There are five levels: N1, N2, N3, N4, and N5, with N1 being the highest level.
The test is divided into three parts:
1) language knowledge (characters, vocabulary, grammar),
2) reading comprehension
3) listening comprehension.
There are no written questions, all questions are mark-response type.
Why Foreigners Take the JLPT|Advantages
More than half of the people who take the JLPT do so for the following reasons: “To enter a graduate school or university when studying abroad” or “To get a job or a raise in salary.
Specifically, many people take the test for the following purposes and advantages
- To meet the requirements for admission to a Japanese university.
- To meet the requirements for employment or to show off their language skills
- To meet the requirements for salary increase or promotion in the company
- To obtain points to receive preferential treatment for “advanced foreign human resources” visas (N1 and N2 only)
- To meet the requirements for taking the Japanese national examination (N1)
- To be exempted from some subjects of the Japanese Junior High School Graduation Certificate Examination (N1, N2)
- One of the conditions for selecting nurse and care worker candidates for the EPA (Economic Partnership Agreement) (N5~N3)
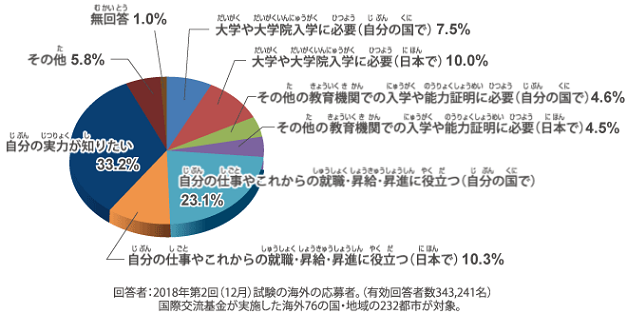
Attributes of JLPT test takers
Refer to the JLPT official website
How to take the exam
If you would like to take the Japanese Language Proficiency Test in Japan, please apply online.
How to apply: After registering for MyJLPT on the JLPT homepage of the Japanese Language Proficiency Test (JESS), you need to log in to MyJLPT and apply from the “JLPT application” screen.
For details, see the website of the Japanese Language Proficiency Test.
My JLPT registration login website
How do you know the result of JLPT?
Those who took the exam in Japan: Please log in to MyJLPT to apply, or apply from your transcript application ID. You can check your JLPT results by logging in to MyJLPT.
You may not have N5 level speaking and writing skills!
Even if you have passed N5, you may not have the same level of speaking and writing ability! The reason for this is that the JLPT is a test of vocabulary, grammar, reading, and listening skills, and does not measure speaking and writing abilities.
Therefore, it is difficult to judge a person’s Japanese language ability based solely on the fact that he or she has passed the JLPT. For example, “Even if I get a certain score on the test, I can’t hold a conversation with a native speaker at all! For example, “Even if I get a certain score on an exam, I can’t hold a conversation with a native speaker!
Summary [Japanese Language Proficiency Test N5 level]
- JLPT is taken for the purpose of studying abroad, finding a job, getting a raise in salary or promotion, obtaining a visa, etc.
- There are levels from N1 to N5 (N1 is the most difficult).
- The N5 level is “able to understand basic Japanese.
- The passing score for N5 is 80 points, and the passing rate is about 41-56%.
- JLPT is a test that measures knowledge of vocabulary and grammar, reading comprehension, and listening comprehension.
- Note that it does not measure speaking and writing skills.





